Recognize a mosquito
Mosquitoes are generally small insects, measuring between 3 and 10 mm.
The mosquito consists of a body, a pair of scaly wings, six legs, a pair of long antennae and an elongated proboscis.
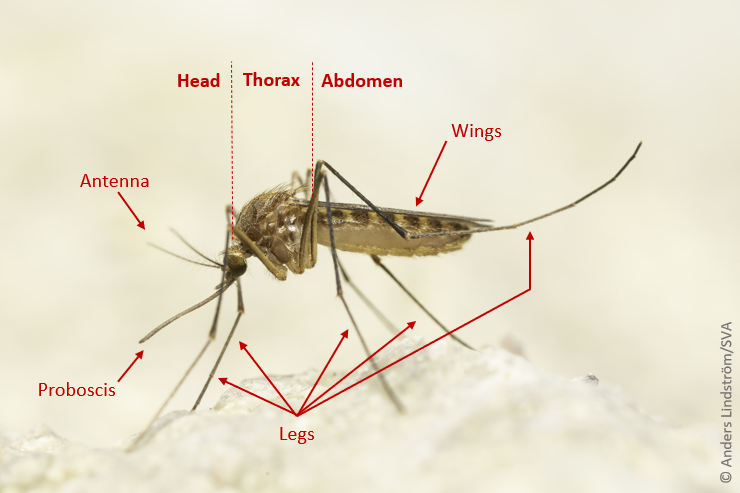
Their body is segmented into three parts:
- head
- thorax
- abdomen
Mosquitoes can be distinguished from other insect species of similar size by the presence of :
- a long, protruding proboscis on males and females
- scales on thorax, legs, abdomen and wings.
The colors and patterns of the scales on the thorax are often used as a guide in identifying different species of mosquito, such as the tiger mosquito, which has a characteristic white line on a black background. When a mosquito is at rest, the wings rest one on top of the other above the abdomen, like a pair of closed scissors.
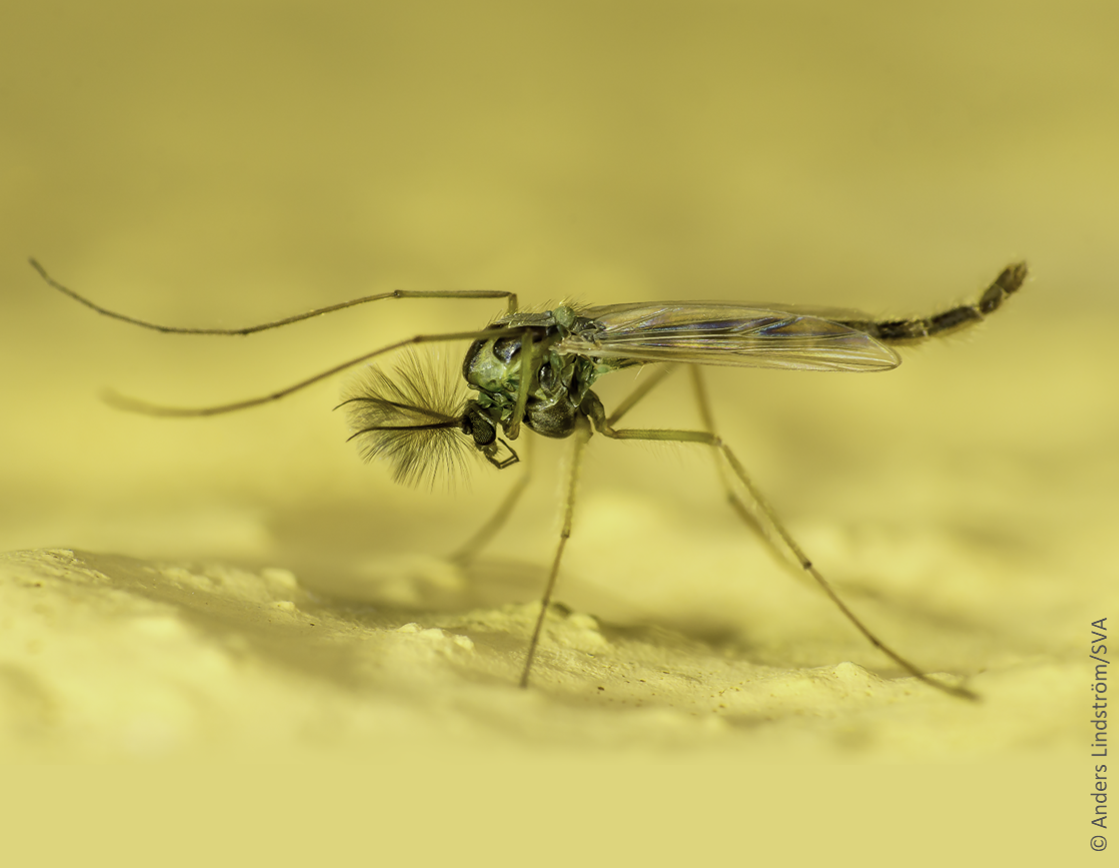
The antennae are used to recognize the sex of the mosquito: males can be recognized by their feathery, fan-shaped antennae, while those of females have short hairs.

|

|
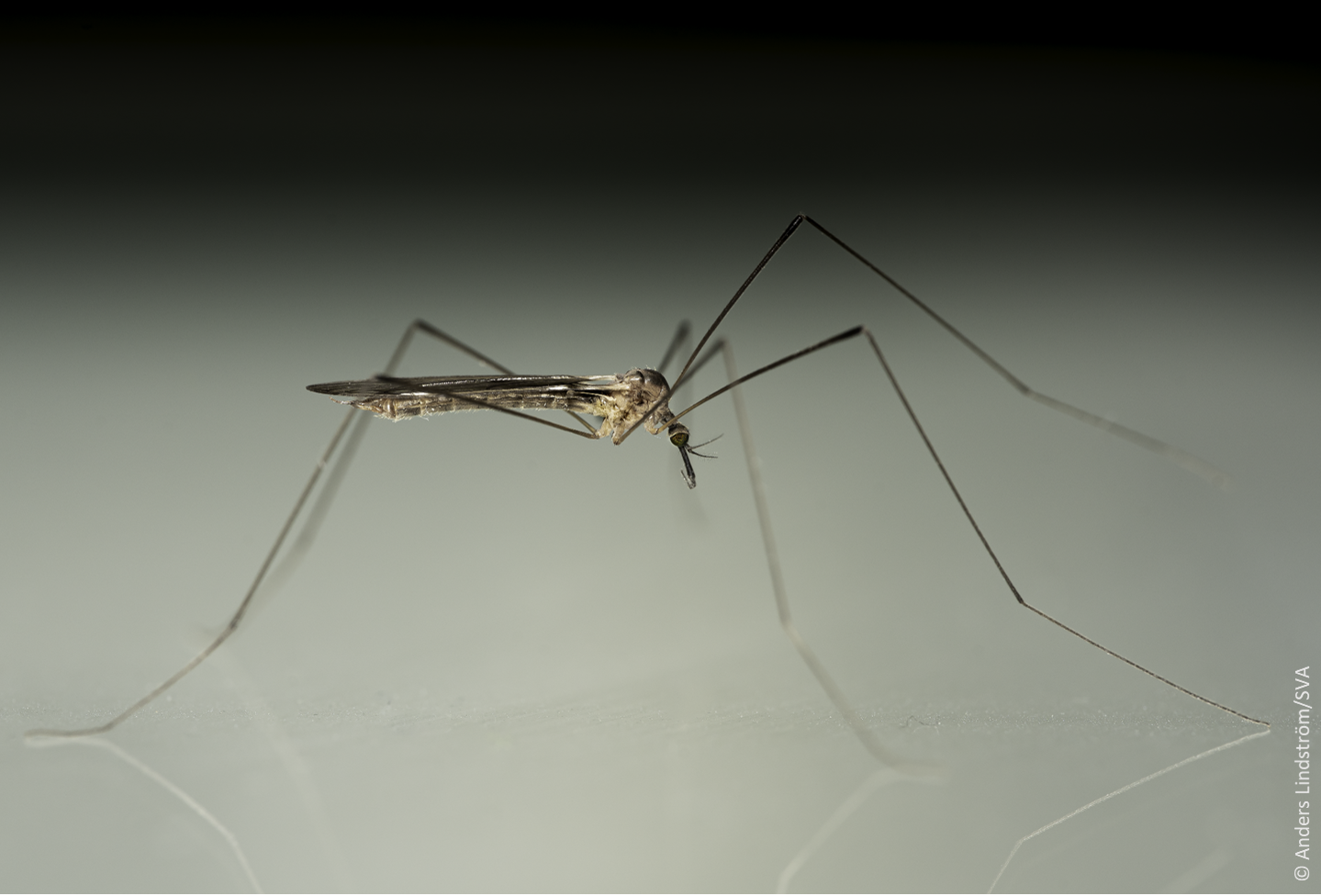
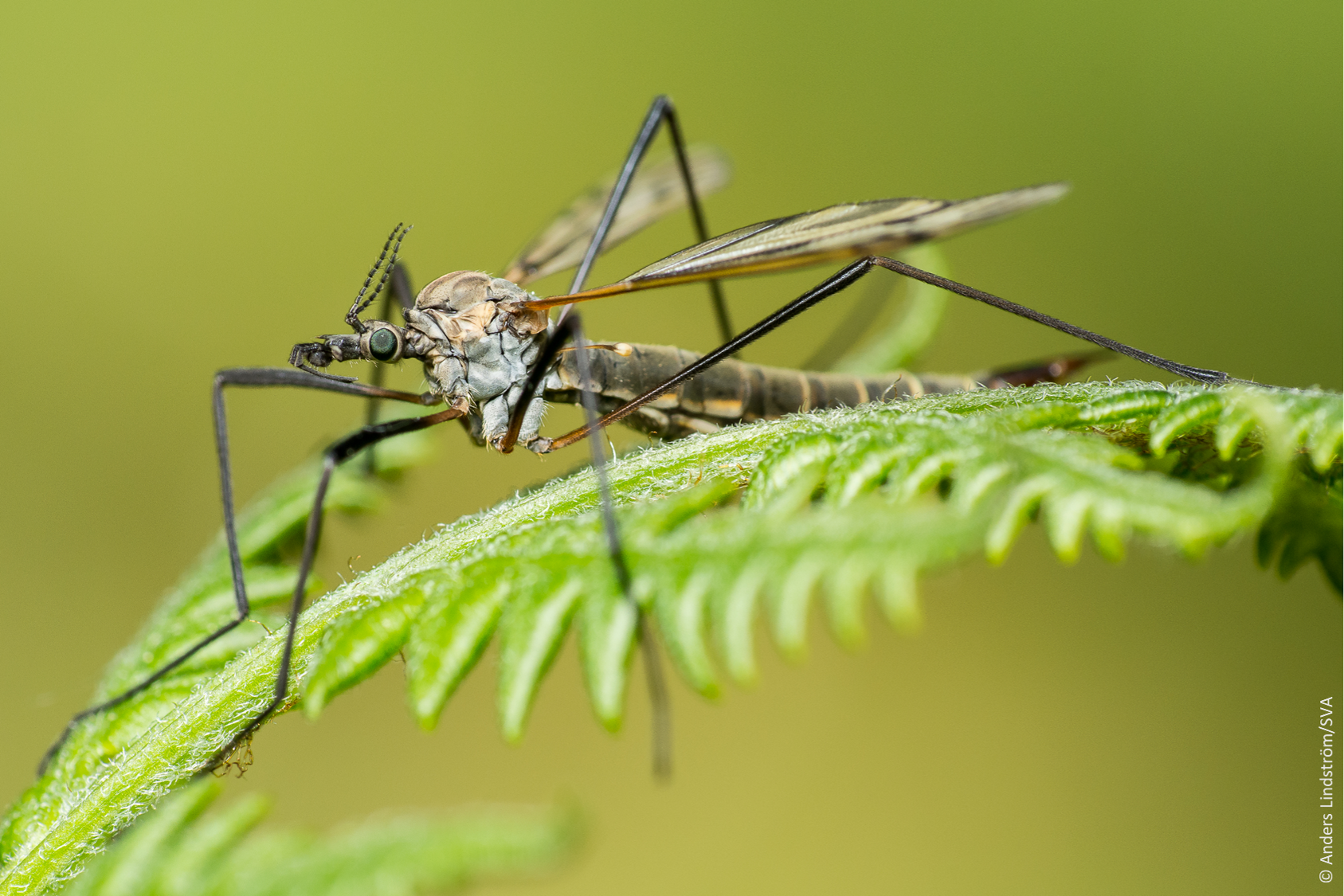
The mosquito is often confused with other insects such as: non-biting midges (Chironomidae), cousins (Tipulidae) and common cave crane flies (Limoniidae). Another characteristic of the mosquito is that its wings are longer than its body, unlike the non-biting midge, for example.

|

|

|
